Cloud Computing in Healthcare: Key Benefits, Risks, and Mitigation Strategies
- DevOps
- March 28, 2024
Curious about how cloud computing is transforming the healthcare industry? Discover the surprising benefits, real-life examples, and potential risks of cloud computing in healthcare. From enhanced data security to improved patient care, learn why the healthcare cloud computing market is booming and how to navigate its challenges. Dive in to see the different types of cloud computing in healthcare, and how they are revolutionizing its processes!
From consulting a doctor online through telemedicine applications to upgrading patient observation through a seamless cloud and IoT-connected healthcare observation system with computer vision capabilities, the healthcare industry is thriving toward advanced digital transformation.
Around 92% of healthcare institutions have achieved better patient experience through digital transformation. But do you even know how all of these healthcare processes can be managed digitally? It all became possible thanks to the implementation of cloud computing in healthcare.
Forrester’s study revealed that 73% of healthcare organizations use cloud computing in place. In the duration of a year, increasingly 45% of healthcare organizations have spent more than $5 million for the adoption of public cloud platforms only. Why are healthcare organizations moving to the cloud?
Most of the healthcare institutes choose cloud systems to achieve improved privacy, lowered expenses, and better patient care through remote operation and collaboration. The implementation of cloud computing in healthcare brings new ways to enhance the functionality of IT systems.

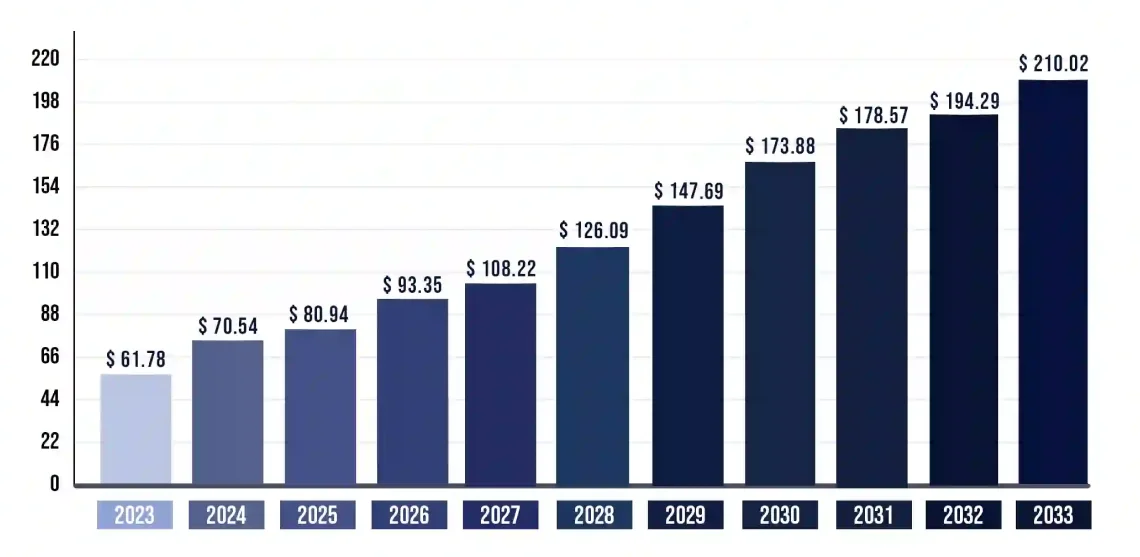
Hence, the global healthcare cloud computing market size is estimated to grow from $61.78 billion (in 2023) to $210.02 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 13.01% for the forecasting period of 2024-2033.
Want to know how the use of cloud computing in healthcare can benefit the industry, what are the risks associated and how to mitigate such? Then, you’ve landed on the right blog that aims to answer all your queries before investing in cloud computing for your healthcare digital transformation mission.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing in healthcare refers to the delivery of computing services – such as storage, processing power, and software applications – over the internet through remote server implementation, specifically tailored to meet the unique demands of the healthcare sector.
This model enables healthcare organizations to securely and seamlessly store and share vast amounts of patient data, facilitate real-time collaboration among healthcare providers, and deploy innovative applications that enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
The Adoption Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The adoption of cloud computing in healthcare offers a range of significant benefits that can transform how healthcare providers deliver care, manage data, and operate their practices.
Here are some key advantages of cloud computing in healthcare:
1. An Affordable Solution for Storing Healthcare Data
Healthcare providers produce massive amounts of digital data every year. These include lab tests, insurance claims, EMRs, and prescriptions. Cloud technology helps handle that data efficiently. When cloud computing offers more data storage, cloud-based analytical tools can use data more and change it into meaningful information.
2. Enhanced Support for Telemedicine
The cloud enables the deployment of telemedicine platforms that allow patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely. Cloud-based telehealth systems help to share healthcare data, offer patient health insurance during treatment, prevention and recovery, and enhance availability.
This capability expands access to care, particularly for patients in remote or underserved areas, and supports a more patient-centered approach to healthcare.
Want to build a telemedicine app to offer better remote patient care? Read our blog on how to develop a Telemedicine app like Doctor on Demand.
3. Improved Patient Experience With Real-Time Data Accessibility
Doctors can ensure better patient involvement by providing real-time access to lab test reports, medical information, and doctors’ notes with the use of cloud computing in healthcare practices. It helps patients maintain their health more precisely with better knowledge.
4. Streamlined Administrative Processes
Cloud-based healthcare solutions can help to automate administrative tasks such as billing, scheduling, and patient management. This further leads to improved efficiency by
automating administrative tasks such as billing, scheduling, and patient management through administrative burden for the healthcare staff.
Thanks to this, healthcare professionals can be more focused on patient care and other critical activities.
5. Enhanced Collaboration With Cloud-based EMR Solutions
The application of cloud technologies in healthcare improves collaboration. Due to the EMR in the cloud, patients no longer require individual medical records while visiting a doctor.
Doctors even can share data, check earlier consultations with other healthcare professionals. It saves time for doctors and patients and aids in more precise diagnosis and treatment.

6. Offers Interoperability For Healthcare Professionals
Interoperability is all about creating data integrations via the healthcare system, regardless of the source of data storage. Cloud solutions enable interoperability in healthcare and make patients’ information accessible for flexible distribution and getting insights to facilitate healthcare delivery.
Cloud computing in healthcare allows medical professionals to access patients’ medical data collected from numerous sources, distribute it among primary stakeholders, and deliver on-time protocols.
7. Proven Disaster Recovery and Backup
Cloud computing provides reliable backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that critical healthcare data is protected and can be quickly restored in the event of a system failure or other disruptions. This minimizes the risk of data loss and enhances overall data resilience.
Disaster recovery and backup is also one of the clauses of HIPAA compliance, which you know. Read Our expert guide on how to make your healthcare application HIPAA-compliant.
Types of Cloud Computing
The types of cloud computing can be classified from two viewpoints: Deployment and Distribution.
1. Distribution Model
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises installations.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Offers virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with underlying infrastructure.
These are also known as cloud computing services. Need help in choosing the right cloud system for your healthcare software solution? Our blog on IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS can help.
2. Deployment Model
- Community: Community clouds are shared by multiple organizations with similar requirements, such as healthcare providers within a specific region or network.
- Private: Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, either hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. They offer a higher level of control and security.
- Public: Public clouds are operated by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These platforms offer scalable resources and services over the internet.
- Hybrid: Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
These are also known as cloud computing environments. Want to know more? Read our blog on types of cloud computing for better understanding.
There are ways you can also utilize different cloud computing environments in the same application in the hybrid scenario.
When two cloud environments are used together – what will you call it – Multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud? Under the difference with our blog on Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: A Comprehensive Analysis.
What Are the Risks of Cloud Computing In Healthcare?
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits for healthcare applications, such as improved data accessibility and cost efficiency, there are several potential implementation risks associated with data and privacy that organizations must consider. Here’s an overview of the potential risks associated with cloud computing in healthcare:
1. Healthcare Data Security and Privacy Risks
Storing sensitive patient data in the cloud raises concerns about data security and privacy. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber-attacks can compromise patient information. Data breaches can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal issues, and loss of patient trust.
There are more than 5,887 data breaches in the healthcare sector alone have been reported between 2009 and 2023. The numbers from 2024 are still incoming – which is currently at 387 data breach reports.
This requires businesses to hire cloud computing experts who have knowledge of cloud security best practices to provide a cloud solution that does not make them fall for data breaches.
2. Restricted Ecosystem
The only acceptance of cloud solutions in healthcare cannot make the whole industry productive and efficient. To reap the benefits of this cloud computing in healthcare, healthcare organizations need to use Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, and Data Science solutions.
3. Security Challenges
Storing healthcare data is the primary point of adopting cloud technology. However, it comes with security risks also. Due to the primary cloud setup, a company’s data shared on the server with other companies may not be properly segregated. Plus, the remote systems intended to individualize them may fail. It causes a situation where healthcare agencies fail to adopt cloud solutions.
4. Issues in Adopting Technologies
Transitioning from a legacy framework to cloud technologies requires a comprehensive transformation of the entire task management process. It’s essential for healthcare agencies to ensure that their teams understand how these new tools will enhance their daily operations.
They may ask or choose the Cloud-based healthcare solution providers that offer training during the handover, empowering clients to fully leverage the benefits of the new system.
At the time of project handover, MindInventory never fails to provide training to customers and their teams, ensuring they understand the software solutions and can fully maximize their benefits.
5. Compliance Challenges
Implementing cloud computing in healthcare can be a complicated has many compliances. Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict regulatory requirements regarding data handling, such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. There are possibilities that you may find it challenging to adhere to all compliance standards alone, but taking the help of cloud computing experts with knowledge of such compliances in healthcare, can get the implementation done seamlessly.
6. Vendor Lock-In
Using cloud services from a single provider can create dependency, making it difficult to migrate to other platforms or integrate with different systems. That’s where businesses face vendor lock-in.
Vendor lock-in can limit flexibility and hinder the ability to switch providers if needed. Organizations should consider cloud strategies for data portability and interoperability to reduce dependency on a single vendor.
7. Cloud Cost Management Issues
While cloud computing can be cost-effective, managing and predicting costs can be challenging, especially with variable usage patterns and unexpected charges.
Unexpected costs can strain budgets and affect financial planning. Hence, businesses should get help from cloud computing experts to get the cloud cost optimization strategy that helps them use its services effectively within their budget.
How to Mitigate Risks Associated with Building Healthcare Cloud Computing Solutions?
Building cloud-based healthcare solutions involves several risks, but with careful planning and best practices, these risks can be effectively managed. Here’s a guide on how to avoid common associated risks of cloud computing in healthcare:
1. Decide Your Objectives
First, understand the requirements like what type of cloud systems your healthcare business seeks for. Identify, what’s your reason behind choosing a cloud ecosystem for your healthcare business. Some of the popular reasons behind moving the workloads to cloud-based systems include:
- Saving expenses
- Healthcare compliance management
- Security improvement
- Data protection and better backups
- Portability
- Easy accessibility
Understanding the key objectives helps you communicate with your cloud services provider. And they can provide tailored cloud engineering solutions according to your business requirements.
2. List out the Things to Switch to the Cloud
You may have many processes to switch to the cloud, but you need to understand that some particular functions need this improvement. Hence, analyze the current pipeline of your healthcare organization and recognize the obstacles that are preventing quality medical delivery or holding back your healthcare team’s operation.
After assessing your company’s processes, give importance to the immediate switch to the cloud to reap the topmost benefits. Moreover, it will help better communicate with the technology vendor and measure the precise time needed for the technical delivery.
3. Measure the Particular Investments
Switching to the cloud needs specific spending. Hence, understand whether your business can afford such investments. The primary expenditure includes paying tech experts engaged in the whole transfer process. You can:
- Outsource Jobs to Offshore Cloud Services Provider: It’s a trustworthy choice that offers security, convenience, and reasonable rates. However, you must be ready for potential language issues.
- Create an In-House Technical Team: It’s a complex process as you need to hire employees and pay a high amount to every specialist. However, simultaneously, you can control the entire transfer process.
- Hire Freelancers: It is not preferable to share a medical organization’s data with freelancers. Also, there might be chances of them leaving your project mid-way. Instead of this, you go for dedicated hiring services offered by reputed IT companies.
4. Ensure Cloud Data Security and Privacy
Data is vulnerable in any situation, whether at rest or in transition. This is evident from cloud computing statistics on security, which reveal that nearly 80% of companies using cloud services experienced at least one security incident last year. Considering its security criticality, it is important to encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access and breaches, following cloud security best practices.
It also creates a need to employ strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Once all implementations are done, regular check-ins for the security assessment and audits are a must to identify and address cloud-based healthcare solution vulnerabilities.
5. Maintain Compliance with Regulations
Select cloud service providers that comply with relevant regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, or other local data protection laws. Regularly check and stay updated with changing compliance clauses and requirements and ensure that your healthcare cloud solutions adhere to these standards as well.
Also, have a designated compliance audit team in place that can assist you in maintaining detailed records of compliance practices and conducting regular reviews to ensure ongoing adherence.
6. Ensure to Have an Effective Backup and Recovery Strategies
Ask your cloud services provider and cloud-based healthcare solution management team to schedule regular, automated backups of all critical data to prevent loss from accidental deletion or corruption.
Ensure that you have a comprehensive disaster recovery plan so you can quickly restore data and services in case of an outage or failure.
As a part of cloud management best practice, it’s a must to have data backup across different cloud regions and availability zones and multiple locations to get instant backup of healthcare data in case of an outage caused by various reasons.
7. Employee Multi-Cloud Strategy
Having your healthcare application deployed in a single cloud platform can lead you to vendor lock-in when you want to reap the benefits of other cloud platforms. That’s where choosing a multi-cloud strategy helps to avoid dependency on a single vendor and enhance flexibility.
For a deeper understanding of challenges in healthcare software development, regardless of the technology, explore our detailed healthcare software development guide.
Real-World Examples Of Cloud Computing In Healthcare
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone in healthcare, enabling innovative solutions that enhance patient care, streamline operations, and support medical research. Here are some real-world examples of how cloud computing is being utilized in the healthcare industry:
1. AZ Delta – Equips EMR With Cloud and ML Abilities
AZ Delta – the large regional hospital in Belgium, was challenged with managing its medical data at a scale as it was planning to offer to improve healthcare services. It had already digitized its healthcare data, but it was all scattered across locations. Its data included complex and varied types of information like the EMR of a single patient would have thousands of data points. This institute consults over 650,000 patients a year.
- Considering its need for centralized and power data processing needs, it adopted cloud services to store sensitive medical data within a Virtual Private Cloud with 3-factor authentication and cloud identity.
- That cloud leverages BigQuery to organize and analyze hundreds of millions of data points at speed.
- Further, that data is to be processed with ML algorithms to cater to the unique healthcare needs of different patterns.
Thanks to the right choice of cloud service provider – Google Cloud Provider and strategic cloud implementation in its healthcare software solution, AZ Delta now has a system that can run a query within 15 seconds rather than 15 minutes, which it used to do with traditional systems. Moreover, it has also cleaned data for 50,000 patients with around half a million data points with ease and speed.
2. Pfizer – Utilizes Cloud Computing Capacity For COVID-19 Vaccine Development
Pfizer – a globally leading pharmaceutical and biotech industry, wanted to develop a dedicated scientific data cloud (SDC). It partnered with AWS cloud with a requirement to rapidly access biotech data, which used to take weeks or even months.
In collaboration with AWS, Pfizer slowly moved its applications and server infrastructure to the AWS cloud. There were 1,000+ applications and 8,000+ servers; it moved all of that to the cloud within 42 weeks – which was also considered one of the fastest migrations to the cloud for a company like Pfizer’s size.
Because of this, it also saved $37 million and carbon blueprints significantly (approx. 4,700).
Further, this step for cloud adoption helped Pfizer at the time of COVID-19, when it needed advanced cloud computing resources and capacity for the analysis stage of vaccine development.
3. Teladoc – Useas Cloud Infrastructure to Offer Real-time Doctor-Patient Video Conferencing
Teladoc Health is a leading telemedicine provider that uses cloud-based services to connect patients with healthcare professionals for virtual consultations. The cloud infrastructure supports real-time video conferencing, secure data exchange, and remote monitoring, making healthcare more accessible, especially in underserved areas.
As it uses a robust cloud infrastructure, it can offer its users 100% network availability. Because of this, it can also be easily integrated with all sorts of EMRs.
Over 50 U.S. health plans use Teladoc Health Services for better patient experiences – being used by Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and multiple Blue Cross Blue Shield plans nationwide.
Additionally, from 40%+ Fortune 500 to small businesses, labor unions, and public-sector employers offer Teladoc virtual care services to their employees.

How MindInventory Can Be Your Cloud Partner For Your Healthcare Business
Implementing cloud computing in healthcare can shape the industry’s future in several ways. From reducing expenses or time to providing conveniences, scalability, and enhancing collaboration among healthcare researchers, cloud solutions have many things to offer.
If your organization lacks specialists, hire a healthcare software development company to adopt cloud solutions and overcome technical issues.
FAQs About Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing plays an essential role in the healthcare industry by enabling secure data storage, improving patient care through real-time access to health records, supporting telemedicine services, and facilitating large-scale data analytics. It helps healthcare organizations streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration among healthcare providers.
You can utilize cloud computing in the healthcare ecosystem for applications like managing electronic health records (EHRs), enabling telehealth and remote patient monitoring, supporting medical research with big data analytics, and improving collaboration among healthcare professionals.
The best cloud platform for healthcare often depends on specific needs, but leading options include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
The biggest concern with cloud computing in healthcare is data security and privacy. Protecting sensitive patient information from breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber-attacks is paramount. Healthcare organizations must ensure that cloud providers adhere to strict security standards and regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, to safeguard patient data.
Healthcare organizations may expect cloud computing to help them with advanced AI-driven diagnostics, personalized medicine suggestions, real-time patient monitoring, remote patient monitoring, and many other ways. As the healthcare industry evolves, cloud solutions will play a key role in enabling more connected, data-driven care.
Healthcare organizations are moving to the cloud to improve operational efficiency, enhance data accessibility, and reduce costs. Cloud computing allows for scalable storage, supports telehealth initiatives, and facilitates collaboration among healthcare providers. It also enables better data management and analytics, helping organizations make informed decisions and deliver more personalized patient care.













